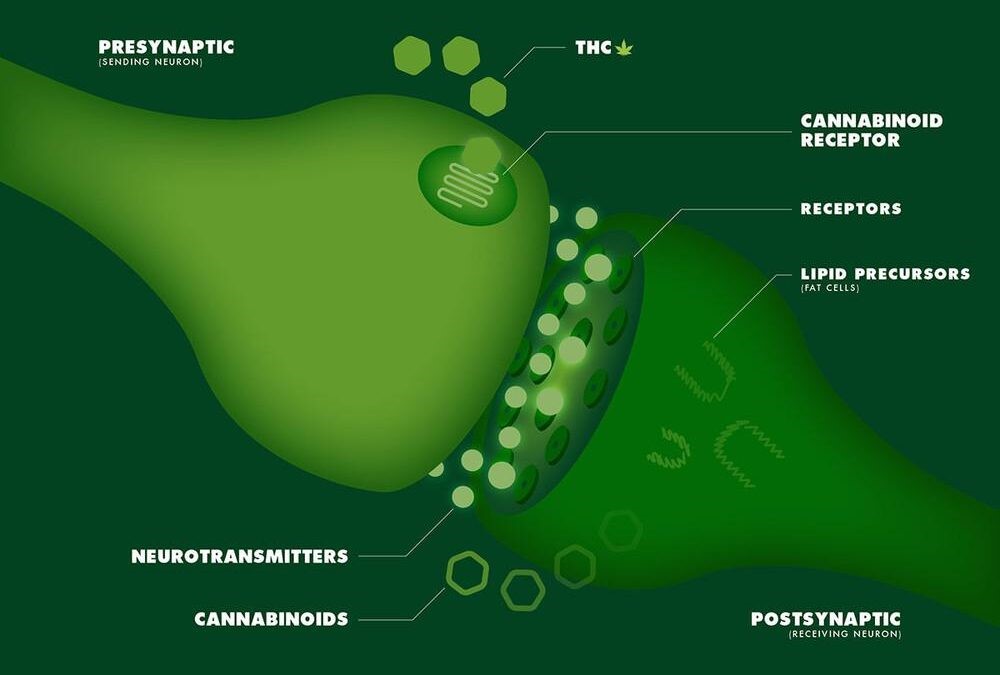
The Endocannabinoid System was discovered in 1992 at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.The ECS functions as a neuromodulatory system working to help develop the Central Nervous System (CNS), synaptic plasticity, and acts in response to environmental and internal attacks. It is involved in regulating the immune response, cell communication, metabolism, appetite, memory and more.
The ECS is made up of endogenous cannabinoids (endocannabinoids), cannabinoid receptors and the enzymes responsible for the building and breakdown of endocannabinoids. Endogenous cannabinoids are lipids that engage with cannabinoid receptors and influence the human body’s physiology. For example, when THC combines with its receptor we begin to feel its psychoactive effects. It is the job of endocannabinoids to help the body maintain homeostasis (balance within the body).
There are two main cannabinoid receptors that have been studied so far, CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are correlated with the psychoactive effects of cannabis. They have so far been located in the brain, CNS, and the reproductive systems of both males and females.
CB2 receptors have been found to work on regulating the immune function and inflammation. They can be found distributed through the immune system.
Author : Chloe Fox @puffpuffplant_
Editor: Corwin Nicasio