Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in plants such as cannabis. They are sometimes referred to as phytocannabinoids, as they are produced by plants. Some other plants that contain cannabinoids include broccoli, echinacea, and cocoa. Once consumed, cannabinoids are utilized by the endocannabinoid system, where their purpose is to help the body regulate itself and maintain optimal homeostasis.

The Endocannabinoid System
This intricate system is developed in the earliest stages of embryonic development. It is made up of receptors, endogenous glands “endocannabinoids”, synthesizing and degrading molecules, and transporter molecules.
There are two main endocannabinoids researched at this point:
2- Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG): Found to be present in breast milk. 2-AG is one of the most important components of the Central Nervous System (CNS) as it works to activate the CB1 receptor.
Anandamide (AEA): Helps to regulate functions such as appetite, pleasure, memory, sleep, and pain relief.
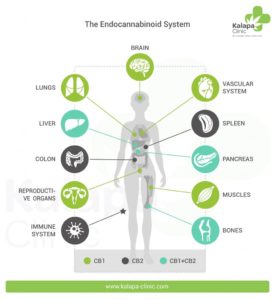
Cannabinoid Receptors
The purpose of cannabinoid receptors is to initiate action of the central and peripheral nervous systems from the cannabis plant. Currently, we are aware of two different cannabinoid receptors- CB1 and CB2.
CB1: This receptor is found primarily in the brain (central nervous system), but can also be found in the gonads, kidneys, lungs, and liver. The CB1 receptors moderate the psychoactive effects of delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which they have a high affinity of binding to. Through a series of channels (inhibition of neurotransmitters and activation of potassium MAP channels), these receptors work to reduce pain, regulate gene expression and cell survival.
CB2: There is some evidence of CB2 in the brain, but so far, the majority of its receptors have been located in the immune system and hematopoietic cells (which give birth to new blood cells). The fact that this receptor is found so heavily in the immune system indicates that it has the potential to act as an immunomodulator (helping to regulate the immune system and reduce levels of inflammation).
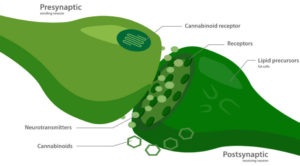
Enzymes
There are two main enzymes that are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they have fulfilled their duties; fatty acid amide hydrolase (breaks down AEA) and monoacylglycerol acid lipase (breaks down 2-AG).
One of the greatest benefits of legalization is the abundance of research that is now able to be done on cannabis and the endocannabinoid system. More research is needed, but we can’t wait to continue to learn more about this incredible plant and how it interacts with our bodies!
Sources:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19647111/
https://summitreleaf.com/2020/05/04/the-endocannabinoid-system/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/cannabinoid-receptor
https://www.labroots.com/trending/cannabis-sciences/8646/role-cb1-receptor-relief-pain


